Ready to get fit and active? Look no further, because we’ve got you covered with our article on the “What Are The 4 Main Exercises?” Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast or just starting your health journey, it’s important to know the core exercises that will help you achieve your goals. In this article, we will explore the four main exercises that are essential for a well-rounded fitness routine. From strength training to cardiovascular workouts, we’ve got all the information you need to get started on your fitness journey. Get ready to sweat and feel the burn as we guide you through these key exercises!
This image is property of www.nia.nih.gov.
Review contents
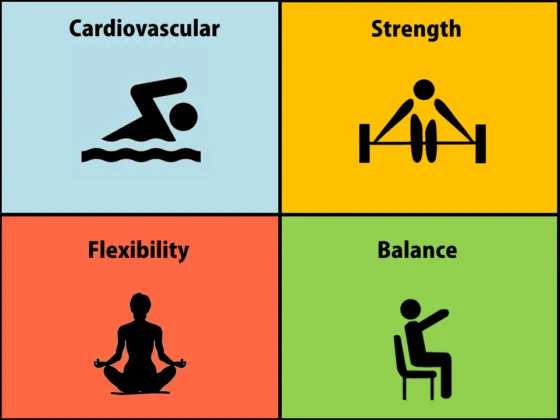
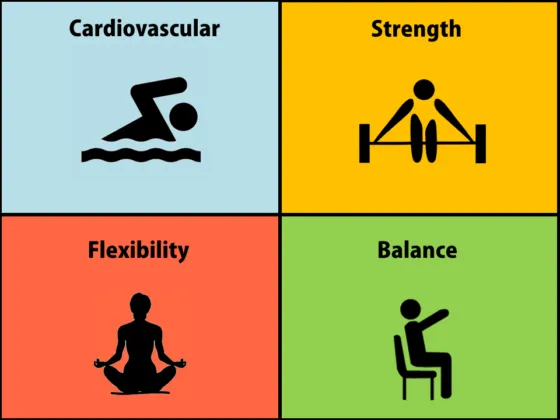
Cardiovascular Exercises
Definition of Cardiovascular Exercises
Cardiovascular exercises, also known as aerobic exercises, are physical activities that increase the heart rate and improve cardiovascular health. These exercises focus on increasing the body’s oxygen intake and facilitating the circulation of oxygenated blood to the muscles. They involve rhythmic movements and repetitive motions that engage large muscle groups, such as the legs and arms, over an extended period of time. Examples of cardiovascular exercises include walking, running, swimming, cycling, dancing, and jumping rope.
Benefits of Cardiovascular Exercises
Engaging in regular cardiovascular exercises offers numerous benefits for our overall health and well-being. Firstly, these exercises significantly enhance the health of our cardiovascular system. They improve heart function, strengthen the heart muscle, and enhance the efficiency of the circulatory system. This, in turn, can lower the risk of heart diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes.
Furthermore, cardiovascular exercises are excellent for weight management and can help with weight loss. These exercises burn calories and increase our metabolic rate, leading to the reduction of excess body fat. Additionally, regular cardiovascular workouts improve our body composition by promoting the development of lean muscle mass.
Cardiovascular exercises also have a positive impact on mental health. They release endorphins, which are natural mood-enhancers, leading to reduced feelings of stress, anxiety, and depression. Moreover, these exercises increase oxygen circulation to the brain, promoting mental clarity, focus, and cognitive function.
Examples of Cardiovascular Exercises
There is a diverse range of cardiovascular exercises to choose from, ensuring that everyone can find an activity that suits their preferences and fitness level. Some popular examples include:
-
Walking: This low-impact exercise is accessible to almost everyone. It can be done outdoors or on a treadmill and is a great way to start incorporating cardiovascular workouts into our daily routine.
-
Running: Running is a high-impact exercise that offers both physical and mental benefits. It improves cardiovascular endurance, strengthens muscles, and boosts our metabolism.
-
Swimming: Swimming is a full-body workout that is gentle on the joints. It engages all major muscle groups, enhances cardiovascular fitness, and improves flexibility.
-
Cycling: Whether on a stationary bike or outdoors, cycling is an excellent cardiovascular exercise. It strengthens the lower body muscles, improves cardiovascular health, and can be a fun outdoor activity.
-
Dancing: Dancing is a fun and enjoyable cardiovascular exercise that can be done alone or with a group. It increases heart rate, improves coordination, and enhances flexibility.
-
Jumping Rope: Jumping rope is a versatile exercise that can be done anywhere. It is an excellent way to improve cardiovascular endurance, burn calories, and tone the muscles in the arms and legs.
How to Incorporate Cardiovascular Exercises into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate cardiovascular exercises into our fitness routine, it’s important to start gradually and progress at our own pace. Here are some tips to help us get started:
-
Set realistic goals: Determine how many days a week we want to engage in cardiovascular exercises and set achievable goals for duration and intensity.
-
Choose activities we enjoy: Select activities that we find enjoyable and engaging. This will increase the likelihood of sticking to the routine long-term.
-
Mix it up: Experiment with a variety of cardiovascular exercises to keep it interesting. This can prevent boredom and promote overall fitness by engaging different muscle groups.
-
Schedule workouts: Make cardiovascular exercises a priority by scheduling them into our weekly routine. Treat them as important appointments that we commit to.
-
Warm up and cool down: Always begin with a warm-up to prepare the body for exercise and end with a cool-down to gradually lower the heart rate. This helps prevent injuries and promotes recovery.
-
Monitor intensity: Pay attention to our heart rate during cardiovascular exercises. Aim for a moderate intensity that challenges but doesn’t excessively strain our cardiovascular system.
-
Track progress: Keep a record of our workouts to track progress and stay motivated. This can be as simple as jotting down the duration and intensity of each session.
Remember, consistency is key when incorporating cardiovascular exercises into our fitness routine. Gradually increase the intensity and duration over time to continue challenging the body and reaping the full benefits of these exercises.
Strength Training Exercises
Definition of Strength Training Exercises
Strength training exercises, also known as resistance training or weightlifting, are physical activities designed to build muscle strength, endurance, and size. These exercises involve the use of resistance, such as free weights, machines, resistance bands, or body weight, to provide a challenge to the muscles. By subjecting the muscles to resistance, strength training exercises cause microscopic damage to the muscle fibers. The body then repairs and rebuilds the muscles, resulting in increased strength and hypertrophy.
Benefits of Strength Training Exercises
Incorporating regular strength training exercises into our fitness routine brings a multitude of benefits, both physical and mental. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Increased muscle strength: Strength training exercises target and stimulate specific muscle groups, leading to increased muscular strength and endurance. This is beneficial for performing daily tasks, such as lifting and carrying objects, as well as improving athletic performance.
-
Boosted metabolism: Unlike cardiovascular exercises, strength training exercises have a longer-lasting effect on our metabolism. Building lean muscle mass increases our basal metabolic rate, allowing us to burn more calories even at rest.
-
Weight management: Strength training exercises help us achieve a toned and lean physique by reducing body fat and increasing muscle mass. This can improve body composition and aid in weight loss or weight maintenance.
-
Enhanced bone health: Regular strength training exercises stimulate bone growth and increase bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, especially in older individuals.
-
Improved joint function: Strengthening the muscles surrounding the joints provides extra support and stability, reducing the risk of injuries and improving overall joint health.
-
Better posture and balance: Many strength training exercises target the core muscles and the muscles responsible for maintaining proper posture. Strengthening these muscles can help improve posture and balance, reducing the risk of back pain and falls.
-
Enhanced mental well-being: Strength training exercises, like other forms of exercise, release endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Regular strength training can improve self-esteem, alleviate stress, and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Examples of Strength Training Exercises
Strength training exercises can be performed using various equipment, including dumbbells, barbells, weight machines, resistance bands, or simply using body weight as resistance. Here are some examples of different types of strength training exercises:
-
Squats: Squats target the lower body, primarily the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. They can be performed with just body weight or with added resistance using dumbbells or a barbell.
-
Bench Press: The bench press primarily works the chest muscles (pectoralis major), but also engages the shoulders and triceps. It requires a barbell or dumbbells and a bench for proper execution.
-
Deadlift: Deadlifts are compound exercises that involve multiple muscle groups, including the back, legs, and core. They can be performed with a barbell or dumbbells.
-
Push-Ups: Push-ups are a classic bodyweight exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps. They can be modified to suit different fitness levels by changing the hand placement or performing them on an incline.
-
Bicep Curls: Bicep curls primarily target the biceps muscles. They can be done using dumbbells, resistance bands, or cable machines.
How to Incorporate Strength Training Exercises into a Fitness Routine
Adding strength training exercises to our fitness routine is important for maintaining a well-rounded approach to fitness. Here are some tips on how to incorporate strength training exercises into our routine:
-
Start with a warm-up: Prior to starting strength training exercises, warm up the muscles by performing dynamic stretches or engaging in light cardio activity for 5-10 minutes. A warm-up prepares our muscles for the upcoming workout and reduces the risk of injury.
-
Determine the right intensity: Choose a weight or resistance level that challenges the muscles without compromising proper form. It is essential to maintain the correct technique and gradually increase the load as our strength improves.
-
Include a variety of exercises: Incorporate exercises that target different muscle groups to achieve a well-balanced workout. This will prevent muscle imbalances and ensure overall strength development. Focus on compound exercises, which engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
-
Progress gradually: Gradually increase the intensity, repetitions, or weight used in the exercises over time. This progressive overload stimulates muscle growth and prevents plateaus.
-
Rest and recovery: Allow sufficient rest between strength training sessions. Muscles need time to repair and grow stronger after each workout. Aim for 48 hours of recovery between sessions targeting the same muscle group.
-
Listen to your body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain during exercises. If something feels wrong, modify the exercise or seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional to ensure proper form and technique.
-
Combine with other forms of exercise: Strength training exercises can be combined with cardiovascular exercises, flexibility training, or other activities of interest. This combination helps maintain overall fitness and prevents boredom.
By incorporating strength training exercises into our fitness routine, we can reap the many benefits they offer and achieve a well-rounded and strong physique.
Flexibility Exercises
Definition of Flexibility Exercises
Flexibility exercises, also known as stretching exercises, focus on improving the flexibility, mobility, and range of motion of our muscles and joints. These exercises involve elongating and lengthening the muscles to improve their elasticity and reduce muscle tightness. Flexibility exercises can be static, where a stretched position is held for a period of time, or dynamic, involving controlled movements that actively stretch the muscles and joints.
Benefits of Flexibility Exercises
Incorporating regular flexibility exercises into our fitness routine offers numerous benefits for our physical health and overall well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Improved muscle flexibility: Flexibility exercises help lengthen and elongate the muscles, improving their overall flexibility and suppleness. This can enhance our ability to perform everyday activities with ease and without strain or discomfort.
-
Increased range of motion: Regular flexibility exercises improve the range of motion of our joints. This allows for fluid and unrestricted movement, reducing the risk of joint or muscle injuries and enhancing athletic performance.
-
Enhanced posture: Flexibility exercises can help correct poor posture by elongating tight muscles and promoting optimal alignment of the spine and joints. This can reduce the risk of back pain and promote better body mechanics.
-
Reduced muscle soreness: Stretching after a workout can help alleviate muscle soreness and stiffness caused by exercise. It increases blood flow to the muscles and aids in the removal of metabolic waste products, promoting faster recovery.
-
Improved circulation: Flexibility exercises improve blood flow to the muscles, supplying them with oxygen and nutrients. This helps maintain proper muscle function and supports overall cardiovascular health.
-
Enhanced relaxation and stress relief: Flexibility exercises promote relaxation by reducing muscle tension and promoting a calm state of mind. The focus required during stretching exercises can help clear the mind and reduce stress levels.
Examples of Flexibility Exercises
There are several types of flexibility exercises that target different muscle groups and joints. Here are some examples of commonly performed flexibility exercises:
-
Static Stretching: This involves holding a stretch for a specific period of time, usually 15-30 seconds. Examples include hamstring stretches, toe touches, and chest stretches.
-
Dynamic Stretching: Dynamic stretching involves controlled movements that actively stretch the muscles while in motion. Examples include arm circles, walking lunges, and high knees.
-
Yoga: Yoga combines flexibility exercises with breathing techniques and mindfulness. It includes a wide variety of poses and stretches that target different muscle groups and promote flexibility, balance, and relaxation.
-
Pilates: Pilates exercises emphasize core strength and flexibility. They often involve controlled movements combined with breathing patterns to enhance overall body flexibility and muscle tone.
How to Incorporate Flexibility Exercises into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate flexibility exercises into our fitness routine, consider the following tips:
-
Warm up before stretching: Always warm up the muscles and joints with light aerobic exercise, such as walking or jogging, before starting flexibility exercises. This increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares them for stretching.
-
Stretch after workouts: Perform flexibility exercises after completing a workout session. The muscles are warm and more receptive to stretching, maximizing the benefits.
-
Start gradually: Begin with gentle stretches and gradually increase the intensity and duration over time. Avoid bouncing or overstretching, as this can lead to muscle strain or injury.
-
Target major muscle groups: Focus on stretching major muscle groups, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, calves, chest, back, and shoulders. Hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds without bouncing or forcing the movement.
-
Breathe and relax: Remember to breathe deeply and relax into each stretch. Exhaling during the stretch can help release tension and allow for a more effective stretch.
-
Incorporate stretching breaks: Take short stretching breaks throughout the day, especially if we have a sedentary lifestyle or work at a desk for extended periods. Simple stretches, like neck rolls or shoulder stretches, can help relieve muscle tension and improve circulation.
-
Try different types of stretching: Explore various types of flexibility exercises, such as yoga or Pilates, to improve flexibility, balance, and body awareness. Attending a class or following online tutorials can help us learn proper techniques.
Remember, flexibility exercises should not cause pain or discomfort. Stretching should feel gentle and relaxing. If we have any existing injuries or medical conditions, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new stretching routine.
Balance and Coordination Exercises
Definition of Balance and Coordination Exercises
Balance and coordination exercises aim to improve our ability to control and maintain balance, as well as enhance coordination between different body parts. These exercises challenge our proprioceptive system and target the muscles responsible for stability and coordination. By incorporating balance and coordination exercises into our fitness routine, we can enhance our overall physical performance, reduce the risk of falls or injuries, and improve our body’s control and awareness.
Benefits of Balance and Coordination Exercises
Incorporating regular balance and coordination exercises into our fitness routine offers numerous benefits for our physical and mental well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Enhanced body control and awareness: Balance and coordination exercises challenge our body’s proprioceptive system, which is responsible for our ability to sense and control our body position and movement. Regular practice improves body awareness and helps us move with precision and control.
-
Reduced risk of falls and injuries: By improving balance and coordination, we become more stable and less prone to falls or injuries. This is especially important for older adults, who may experience a decline in balance and coordination with age.
-
Improved athletic performance: Balance and coordination exercises enhance our ability to perform specific movements and skills required in various sports and physical activities. This can lead to improved athletic performance and efficiency.
-
Strengthened core muscles: Many balance and coordination exercises engage the core muscles, which are essential for maintaining proper posture and stability. Strengthening these muscles can help alleviate back pain and improve overall core strength.
-
Enhanced brain function: Balance and coordination exercises require focus, concentration, and coordination between different body parts. Regular practice can improve neural connections and cognitive function, benefiting overall brain health.
-
Increased body stability: Balance exercises target the muscles responsible for balance and stability, including the muscles of the legs, hips, and core. Strengthening these muscles improves our ability to maintain stable positions during various activities.
Examples of Balance and Coordination Exercises
There are numerous balance and coordination exercises that target different muscle groups and challenge our body’s ability to maintain stability. Here are some examples:
-
Single-Leg Stands: Stand on one leg, lifting the opposite leg slightly off the ground. Hold the position for 30 seconds to a minute, then switch legs. This exercise improves balance and strengthens the muscles of the standing leg.
-
Yoga Tree Pose: Stand with feet together and shift the weight onto one leg. Place the sole of the opposite foot on the inner thigh of the standing leg, above or below the knee. Hold the pose for 30 seconds to a minute, then switch legs. This exercise improves balance, stability, and hip flexibility.
-
Heel-to-Toe Walk: Walk in a straight line, placing the heel of one foot directly in front of the toes of the other foot with each step. This exercise challenges balance, coordination, and improves overall body control.
-
Balance Board Exercises: Utilize a balance board or wobble board to perform various exercises, such as squats, lunges, or single-leg stands. These exercises challenge the body’s ability to maintain balance and improve core stability.
-
Crossover Step-Ups: Place one foot on a step or elevated platform and step up, crossing the opposite leg over the midline of the body. Step down and repeat on the other side. This exercise improves coordination and balance, targeting the muscles of the legs and hips.
How to Incorporate Balance and Coordination Exercises into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate balance and coordination exercises into our fitness routine, consider the following tips:
-
Start with the basics: Begin with simple exercises that challenge balance and coordination, such as single-leg stands or heel-to-toe walks. Gradually progress to more advanced exercises as our balance and coordination improve.
-
Include balance and coordination drills: Incorporate specific drills that target balance and coordination, such as ladder drills or cone drills. These exercises can be performed outdoors or indoors using readily available equipment.
-
Integrate balance training into other exercises: Many traditional exercises, such as lunges, squats, or shoulder presses, can be modified to include balance and coordination elements. These modifications can add an extra challenge and engage additional muscles.
-
Practice yoga or tai chi: Participate in yoga or tai chi classes, which emphasize balance, body control, and coordination. These disciplines offer a range of exercises and poses specifically designed to improve balance and coordination.
-
Utilize stability training equipment: Incorporate stability balls, balance boards, or resistance bands into our routine to challenge balance and coordination. These tools add an element of instability, forcing the body to engage stabilizing muscles.
-
Be consistent: Balance and coordination exercises require regular practice to see improvement. Aim to dedicate specific time each week to these exercises and gradually increase the difficulty level as needed.
Remember to always perform balance and coordination exercises in a safe environment, using proper footwear and under adequate supervision, if necessary. Consult with a fitness professional or physical therapist if we have any concerns or specific balance-related goals.
This image is property of cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net.
Low-Impact Exercises
Definition of Low-Impact Exercises
Low-impact exercises are physical activities that put minimal stress on the joints and have a reduced risk of injury compared to high-impact exercises. These exercises involve fluid, controlled movements that avoid excessive pounding or jarring of the joints. Low-impact exercises are suitable for individuals of all fitness levels and ages, including those recovering from injuries, older adults, or individuals with joint conditions. These exercises provide cardiovascular benefits, strengthen muscles, and improve overall fitness without putting excessive strain on the body.
Benefits of Low-Impact Exercises
Incorporating low-impact exercises into our fitness routine offers numerous benefits for our physical health and overall well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Reduced joint stress: Low-impact exercises minimize the impact on the joints, making them ideal for individuals with joint conditions or those recovering from injuries. They provide a safe option for maintaining cardiovascular fitness and strengthening the muscles without exacerbating joint pain or inflammation.
-
Improved cardiovascular health: Low-impact exercises offer cardiovascular benefits similar to high-impact exercises, such as improved heart health, increased endurance, and enhanced circulation. Activities like swimming or cycling engage large muscle groups and promote cardiovascular fitness.
-
Enhanced muscle strength: Low-impact exercises strengthen the muscles without placing excessive stress on the joints. Resistance exercises using resistance bands or weight machines can improve muscular strength and endurance.
-
Weight management: Low-impact exercises burn calories and increase our metabolic rate, helping with weight loss or weight management. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of various chronic health conditions and improves overall well-being.
-
Improved bone health: Low-impact weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or using elliptical machines, can still help maintain and improve bone density. This is particularly important for individuals at risk of osteoporosis or other bone-related conditions.
-
Reduced risk of injury: Low-impact exercises have a lower risk of injury compared to high-impact exercises. The controlled movements and reduced stress on the joints make them suitable for individuals with a history of joint injuries or chronic pain.
Examples of Low-Impact Exercises
There is a wide range of low-impact exercises to choose from, depending on our preferences and fitness level. Here are some examples:
-
Walking: Walking is a low-impact exercise accessible to almost everyone. It can be done indoors or outdoors and is easy to incorporate into our daily routine. Walking at a brisk pace provides cardiovascular benefits and strengthens the lower body muscles.
-
Cycling: Cycling, whether on a stationary bike or outdoors, is a low-impact exercise that provides cardiovascular benefits and strengthens the leg muscles. It is suitable for individuals of all fitness levels and can be made more challenging by adjusting resistance levels.
-
Swimming: Swimming is a low-impact exercise that engages the entire body and offers cardiovascular benefits without placing stress on the joints. It is particularly beneficial for individuals with joint conditions or those recovering from injuries.
-
Elliptical Machine: Using an elliptical machine provides a low-impact cardiovascular workout that engages the leg and arm muscles. The gliding motion reduces stress on the joints and offers a low-impact alternative to running or jogging.
-
Rowing: Rowing is a low-impact exercise that engages both the upper and lower body. Using a rowing machine or participating in rowing classes provides a full-body workout without placing stress on the joints.
How to Incorporate Low-Impact Exercises into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate low-impact exercises into our fitness routine, consider the following tips:
-
Choose activities we enjoy: Select low-impact exercises that we find enjoyable and engaging. This will increase the likelihood of sticking to the routine long-term. Experiment with different activities to find ones that suit our preferences.
-
Start gradually: Begin with low-impact exercises that match our current fitness level and gradually increase the duration and intensity. Listen to our body and gradually challenge ourselves without pushing too hard or causing discomfort.
-
Mix it up: Incorporate a variety of low-impact exercises into our routine to keep it interesting and prevent boredom. This will engage different muscle groups and promote overall fitness.
-
Combine with other exercises: Low-impact exercises can be combined with strength training exercises, flexibility training, or other activities of interest. This combination helps maintain overall fitness and prevents monotony.
-
Gradually increase intensity: Once comfortable with a particular low-impact exercise, gradually increase the intensity or duration to continue challenging the body. This can be achieved by adding resistance, increasing speed, or trying more challenging variations.
-
Listen to your body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain during low-impact exercises. If something feels wrong, modify the exercise or seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional to ensure proper form and technique.
Remember, consistency is key when incorporating low-impact exercises into our fitness routine. By finding enjoyable activities and gradually increasing the intensity, we can reap the many benefits of low-impact exercises in a safe and effective manner.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
Definition of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is a form of cardiovascular exercise that involves short bursts of intense effort followed by brief recovery periods. This workout method alternates between periods of maximum effort and periods of active recovery. HIIT workouts typically last between 20 to 30 minutes, making them time-efficient and effective for improving cardiovascular fitness and burning calories. The intense bursts of exercise push the body to its limits, maximizing calorie burn and improving endurance.
Benefits of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
Incorporating regular High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) into our fitness routine offers numerous benefits for our physical health and overall well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Efficient calorie burn: HIIT workouts are highly effective for burning calories due to the intense bursts of exercise. The body continues to burn calories and fat even after the workout, thanks to an increased metabolic rate known as the afterburn effect.
-
Improved cardiovascular fitness: The intense intervals in HIIT workouts push the cardiovascular system to its limits, promoting increased oxygen uptake and strengthening the heart. Over time, regular HIIT can lead to improved cardiovascular endurance and enhanced overall fitness.
-
Time-efficient workouts: HIIT workouts are known for their short duration, typically ranging from 20 to 30 minutes. They provide a time-efficient option for those with busy schedules who still want to experience the benefits of cardiovascular exercise.
-
Muscle building and toning: HIIT workouts often incorporate bodyweight exercises or resistance training, promoting muscle building and toning. This helps improve overall body composition while burning fat.
-
Increased metabolism: High-Intensity Interval Training stimulates the production of human growth hormone (HGH), which plays a role in muscle growth, fat burning, and anti-aging benefits. The increased metabolic rate after HIIT workouts helps boost fat loss and supports overall weight management.
-
Enhanced insulin sensitivity: Regular HIIT workouts can increase insulin sensitivity, improving the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. This is beneficial for individuals with or at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Examples of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
There are numerous ways to structure a High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) workout, each involving different exercises and lengths of work and recovery intervals. Here are some examples:
-
Tabata: Tabata is a specific HIIT protocol that consists of 20 seconds of intense exercise followed by 10 seconds of rest, repeated for a total of 4 minutes. This can be done with exercises like burpees, high knees, or squat jumps.
-
30-Second Intervals: Perform exercises at maximum effort for 30 seconds, followed by 30 seconds of active rest or lower-intensity exercise. This can include exercises like mountain climbers, jumping jacks, or kettlebell swings.
-
Pyramid Intervals: Perform intervals of increasing work periods, followed by decreasing rest periods. For example, start with 30 seconds of exercise and 30 seconds of rest, then progress to 45 seconds of exercise and 15 seconds of rest, and finally 60 seconds of exercise and 5 seconds of rest.
-
Circuit Training: Set up a circuit of 6 or more exercises and perform each exercise for a specific duration, such as 40 seconds, followed by a short rest period of 10-20 seconds before moving on to the next exercise. Repeat the circuit for a specific number of rounds.
How to Incorporate High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) into our fitness routine, consider the following tips:
-
Choose exercises wisely: Select exercises that target different muscle groups and can be performed with maximal effort. This ensures a full-body workout and challenges various muscle groups.
-
Warm up properly: Prior to starting a HIIT workout, warm up the muscles and joints with light cardio exercise for 5-10 minutes. This prepares the body for intense exercise and reduces the risk of injury.
-
Start at an appropriate level: Begin with an appropriate intensity level that matches our current fitness level. Gradually increase the intensity or duration as our fitness improves.
-
Maintain proper form: Focus on maintaining proper form and technique during each exercise. This ensures maximum efficiency and minimizes the risk of injury.
-
Alternate high-intensity and recovery: Follow the intervals of high-intensity exercise with periods of active recovery or lower-intensity exercise. This allows the body to partially recover before pushing it to the limit again.
-
Progress gradually: Over time, increase the intensity, duration, or number of intervals in our HIIT workouts. This helps continue challenging the body and prevents a plateau in fitness gains.
-
Combine with other forms of exercise: Incorporate HIIT workouts into our overall fitness routine, along with strength training, flexibility exercises, or low-impact activities. This provides a well-rounded approach to fitness and prevents boredom.
Remember, High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is demanding on the body, so it is important to listen to our body and rest when needed. Consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider before starting HIIT workouts, especially if we have any underlying health conditions or injuries.
This image is property of patch.com.
Plyometric Exercises
Definition of Plyometric Exercises
Plyometric exercises, also known as jump training or plyos, are explosive, high-intensity exercises that involve quick and powerful movements. This type of exercise utilizes the stretch-shortening cycle, which involves rapidly elongating a muscle followed by an immediate shortening contraction. Plyometrics train the muscles to generate maximal force in minimal time, improving power, speed, and overall athletic performance. These exercises typically involve jumping, bounding, and hopping movements.
Benefits of Plyometric Exercises
Incorporating plyometric exercises into our fitness routine offers numerous benefits for our physical health and athletic performance. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Improved power and explosiveness: Plyometric exercises train the muscles to generate maximal force in minimal time. This leads to improved power and explosiveness, which is beneficial for athletic activities that require speed and quick movements.
-
Increased strength and muscle tone: Plyometric exercises involve a rapid contraction of muscles, which recruits a larger number of muscle fibers compared to traditional strength training exercises. This leads to improved muscle strength and enhanced muscle tone.
-
Enhanced athletic performance: Plyometric exercises improve overall athletic performance by enhancing power, speed, agility, and coordination. These exercises mimic movements often used in sports, making them particularly beneficial for athletes.
-
Improved bone density: Plyometric exercises are weight-bearing in nature, which helps to improve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. Regular participation in plyometric exercises can help maintain healthy bones.
Examples of Plyometric Exercises
There are numerous plyometric exercises that target different muscle groups and aspects of athletic performance. Here are some examples:
-
Squat Jumps: Begin in a squat position and explosively jump off the ground, reaching full extension with the hips, knees, and ankles. Land back in a squat position and repeat.
-
Box Jumps: Stand facing a sturdy box or platform. Explode upwards, driving the arms forward, and land softly on top of the box in a controlled manner. Step back down and repeat.
-
Bounding: Perform long, exaggerated leaps forward or laterally, emphasizing speed and power. Bound as far as possible and repeat for a specified distance or number of repetitions.
-
Depth Jumps: Stand on a box or elevated surface. Step off the box, land softly, immediately jump as high as possible upon landing, and repeat.
-
Plyometric Push-Ups: Begin in a push-up position and explosively push off the ground, allowing the hands to leave the surface. Land with soft elbows and immediately repeat.
How to Incorporate Plyometric Exercises into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate plyometric exercises into our fitness routine, consider the following tips:
-
Ensure a good foundation: Plyometric exercises require a certain level of strength and coordination. It is important to establish a solid foundation of strength and stability before incorporating plyometrics into our routine.
-
Warm up properly: Prior to starting plyometric exercises, warm up the muscles and joints with a dynamic warm-up routine. This prepares the body for explosive movements by increasing muscle temperature and joint mobility.
-
Master the technique: Plyometric exercises require proper form and technique to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury. Focus on landing softly, engaging the core, and using the entire body for explosive movements.
-
Start with low-intensity exercises: Begin with low-intensity plyometric exercises to acclimate the body to the demands of explosive movements. As we progress and become comfortable, gradually increase the difficulty level and intensity.
-
Allow for adequate recovery: Plyometric exercises are intense and place significant stress on the muscles and joints. Allow for proper rest and recovery between plyometric workouts to reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
-
Combine with other training methods: Plyometric exercises can be combined with other forms of exercise, such as strength training or cardiovascular workouts, to create a well-rounded fitness routine. This combination helps improve overall athletic performance and prevent boredom.
Always listen to our body and avoid excessive fatigue or pain during plyometric exercises. If we have any underlying health conditions or injuries, it is important to consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider before incorporating plyometric exercises into our routine.
Core Exercises
Definition of Core Exercises
Core exercises target the muscles of the abdomen, hips, lower back, and pelvis, collectively referred to as the core muscles. These exercises focus on strengthening and stabilizing the core, which provides a solid foundation for all movements and improves overall posture and body control. Core exercises often involve dynamic movements that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, promoting functional strength and enhancing athletic performance.
Benefits of Core Exercises
Incorporating regular core exercises into our fitness routine offers numerous benefits for our physical health and overall well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Improved stability and balance: Core exercises strengthen the muscles responsible for stability and balance, leading to improved overall body stability. This can reduce the risk of falls or injuries and enhance overall athletic performance.
-
Reduced risk of back pain: Core exercises help develop a strong and stable core, which supports the spine and reduces the risk of back pain or injuries. Strengthening the core muscles can alleviate existing back pain and improve overall posture.
-
Enhanced functional strength: The core muscles are involved in most functional movements, such as lifting, twisting, or bending. Strengthening these muscles improves overall functional strength, making everyday activities easier and more efficient.
-
Improved athletic performance: A strong core is crucial for optimal athletic performance. It provides a solid foundation for explosive movements, improves agility, and enhances coordination and balance.
-
Enhanced posture and body alignment: Core exercises promote proper posture and alignment by strengthening the muscles responsible for maintaining correct body posture. This leads to improved body mechanics and reduces the risk of postural imbalances or related pain.
-
Improved breathing and diaphragmatic function: Core exercises can help improve breathing patterns and diaphragmatic function. Proper engagement of the core muscles supports optimal breathing mechanics and enhances oxygen uptake during exercise.
Examples of Core Exercises
There are numerous core exercises that target different muscle groups within the core. Here are some examples:
-
Plank: Assume a push-up position, resting on the forearms instead of the hands. Engage the core muscles, maintain a straight line from head to heels, and hold the position for a specific duration.
-
Russian Twists: Sit on the floor with a slight lean back, engage the core, and lift the legs slightly off the ground. Rotate the torso from side to side, touching the floor with the hands or a weight.
-
Bicycle Crunches: Lie on the floor with knees bent and hands behind the head. Bring one knee in towards the chest while simultaneously lifting the opposite elbow towards that knee. Alternate sides in a cycling motion.
-
Bridge: Lie on the back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart. Raise the hips off the ground to create a straight line from the knees to the shoulders. Engage the glutes and hold the position.
-
Transverse Abdominal Exercises: Engage the deep core muscles, specifically the transverse abdominis, by drawing the navel in towards the spine. This can be done in various positions, such as on all fours or standing.
-
Dead Bug: Lie on the back with arms extended towards the ceiling and knees bent at a 90-degree angle. Slowly lower one arm and the opposite leg towards the floor while maintaining core engagement. Return to the starting position and repeat on the opposite side.
How to Incorporate Core Exercises into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate core exercises into our fitness routine, consider the following tips:
-
Choose a variety of exercises: Include a variety of core exercises that target different muscle groups and challenge stability and coordination. This helps promote overall core strength and balanced development.
-
Integrate core exercises into workouts: Add core exercises at the beginning or end of cardiovascular or strength training workouts. This prevents neglecting core work and ensures a comprehensive full-body workout.
-
Focus on proper form: Technique and proper form are essential in core exercises. Focus on engaging the core muscles, maintaining neutral alignment, and avoiding excessive strain on the neck or lower back.
-
Gradually increase intensity: Over time, increase the difficulty level or add resistance to core exercises to continue challenging the muscles. This can be done by using stability balls, medicine balls, or incorporating weights.
-
Pay attention to breathing: Coordinate breathing with core exercises to enhance the engagement and activation of the deep core muscles. Focus on inhaling during the relaxation phase and exhaling during the exertion phase.
-
Be consistent: It is important to be consistent with core exercises to see improvements. Aim to incorporate at least two to three sessions of core exercises into our weekly routine.
Remember, it is essential to listen to our body and avoid overexertion or excessive strain during core exercises. Start with exercises and modifications that suit our current fitness level and gradually progress as our core strength improves. If we have any underlying health conditions or injuries, it is advisable to consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider before starting a new core exercise routine.
This image is property of authortlgray.files.wordpress.com.
Stability Ball Exercises
Definition of Stability Ball Exercises
Stability ball exercises, also known as Swiss ball or exercise ball exercises, involve utilizing a large inflatable stability ball as an exercise tool. These exercises challenge the body’s balance and stability by engaging the core muscles and other muscle groups. Stability ball exercises often target the core, back, legs, and arms, providing a full-body workout that enhances strength, balance, and coordination.
Benefits of Stability Ball Exercises
Incorporating regular stability ball exercises into our fitness routine offers numerous benefits for our physical health and overall well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Improved core strength: Stability ball exercises engage the core muscles in order to maintain balance and stability. This leads to improved core strength, stability, and postural support.
-
Enhanced balance and coordination: Stability ball exercises challenge the body’s balance and proprioception, promoting better balance and overall coordination. Regular practice improves body awareness and the ability to perform movements with control and precision.
-
Increased muscle activation: Stability ball exercises often target multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to increased muscle activation and improved overall muscular strength and tone.
-
Reduced back pain: Stability ball exercises promote proper posture and spinal alignment, which can help reduce back pain and improve spinal stability. By sitting or exercising on a stability ball, the body is forced to engage core muscles to maintain stability and support the spine.
-
Diverse exercise options: Stability balls offer a wide range of exercise options, allowing for a diverse and varied fitness routine. From core exercises to strength training and flexibility exercises, stability balls can be used to target various muscle groups and fitness goals.
Examples of Stability Ball Exercises
There are numerous stability ball exercises that target different muscle groups and aspects of fitness. Here are some examples:
-
Ball Squats: Stand with the stability ball against a wall and position it against the lower back. Slowly squat down, allowing the ball to roll up the back while keeping the knees aligned with the toes. Return to the starting position and repeat.
-
Plank on the Ball: Assume a plank position with the forearms and toes on the stability ball. Keep the core engaged and hold the position, ensuring a straight line from head to heels.
-
Seated Ball Roll: Sit on the stability ball with feet flat on the floor. Lift one foot off the ground and extend the opposite foot forward, maintaining balance and stability on the ball. Alternate legs and repeat.
-
Hip Bridge on the Ball: Lie on the back with the feet resting on the stability ball and knees bent. Lift the hips off the ground, engaging the glutes and hamstrings, and hold the position. Lower the hips back down and repeat.
-
Russian Twist on the Ball: Sit on the stability ball with the feet securely on the ground and knees bent. Lean back slightly and engage the core. Rotate the torso from side to side, touching the floor on each side.
How to Incorporate Stability Ball Exercises into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate stability ball exercises into our fitness routine, consider the following tips:
-
Choose the right size ball: Select a stability ball that matches our height and weight. Ideally, when sitting on the ball, the hips and knees should be at approximately 90 degrees of flexion.
-
Start with basic exercises: Begin with basic stability ball exercises that target core and balance, gradually progressing to more challenging exercises. This allows the body to adapt and build a foundation of stability.
-
Focus on proper form: Pay attention to maintaining proper form and technique during stability ball exercises. Keep the core engaged, maintain proper alignment, and avoid excessive strain on the neck or lower back.
-
Integrate the stability ball into workouts: Incorporate stability ball exercises as part of a well-rounded fitness routine. Use the ball for warm-ups, core workouts, or as a tool for added challenge during strength training.
-
Mix it up: Explore different stability ball exercises to target various muscle groups and aspects of fitness. This helps prevent boredom and ensures a comprehensive and balanced workout.
-
Gradually increase the difficulty: As stability and strength improve, gradually increase the difficulty of stability ball exercises by introducing more complex movements or incorporating weights.
Remember, stability ball exercises may vary in difficulty depending on individual fitness level and coordination. It is important to start with exercises that suit our abilities and progress at our own pace. If we have any underlying health conditions or injuries, it is advisable to consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider before starting a new stability ball exercise routine.
Bodyweight Exercises
Definition of Bodyweight Exercises
Bodyweight exercises are strength and conditioning exercises that utilize the individual’s body weight as resistance, without relying on external weights or equipment. These exercises rely solely on the individual’s ability to control and move their own body through space. Bodyweight exercises are highly versatile, can be performed anywhere, and provide an efficient way to build strength, increase flexibility, and improve overall fitness.
Benefits of Bodyweight Exercises
Incorporating regular bodyweight exercises into our fitness routine offers numerous benefits for our physical health and overall well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Convenience and accessibility: Bodyweight exercises can be performed anywhere, without the need for special equipment or a gym membership. They provide a convenient way to stay active and maintain fitness regardless of location or time constraints.
-
Improved functional strength: Bodyweight exercises engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, promoting functional strength that can be applied to everyday activities. They mimic movements often used in daily life, improving overall body strength and coordination.
-
Enhanced muscular endurance: Performing exercises that utilize body weight as resistance challenges the muscles to work against gravity for extended periods. This improves muscular endurance and stamina, allowing us to sustain physical effort for longer periods.
-
Increased flexibility: Many bodyweight exercises require a full range of motion, promoting flexibility and joint mobility. The natural movement patterns of bodyweight exercises contribute to improved overall flexibility and reduced risk of muscle imbalances or injuries.
-
Improved body awareness and coordination: Bodyweight exercises require significant body awareness, proprioception, and coordination. By utilizing body weight and focusing on controlled, intentional movement, these exercises enhance overall body control and coordination.
-
Cost-effective fitness solution: Bodyweight exercises eliminate the need for expensive equipment or gym memberships, making them a cost-effective way to stay fit and maintain overall health.
Examples of Bodyweight Exercises
There are countless bodyweight exercises that target different muscle groups and aspects of fitness. Here are some examples:
-
Push-Ups: Begin in a plank position with hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Lower the body down by bending the elbows, keeping the core engaged, and return to the starting position. Variations include incline push-ups or diamond push-ups.
-
Squats: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, engage the core, and lower the body into a squat position by bending the knees and pushing the hips back. Return to the starting position and repeat. Variations include sumo squats or jump squats.
-
Lunges: Stand with feet hip-width apart and take a step forward with one leg, lowering the body until both knees form 90-degree angles. Push through the front heel to return to the starting position. Alternate legs and repeat. Variations include reverse lunges or walking lunges.
-
Plank: Assume a push-up position on the forearms, maintaining a straight line from head to heels. Engage the core, hold the position, and keep the body rigid. Variations include side planks or plank knee tucks.
-
Mountain Climbers: Begin in a push-up position with the body in a straight line. Alternate bringing one knee towards the chest while keeping the core engaged and the body stable. Increase speed for a more intense workout.
How to Incorporate Bodyweight Exercises into a Fitness Routine
To incorporate bodyweight exercises into our fitness routine, consider the following tips:
-
Establish a routine: Develop a consistent routine for bodyweight exercises, aiming for at least two to three sessions per week. This ensures regular engagement with bodyweight exercises and maximizes the benefits.
-
Choose a variety of exercises: Include a variety of bodyweight exercises that target different muscle groups and aspects of fitness. This ensures a well-rounded and balanced workout routine.
-
Modify exercises to match fitness level: Start with exercises that suit our current fitness level and gradually progress as strength and coordination improve. Modify exercises to increase or decrease intensity based on individual abilities.
-
Interval training: Incorporate bodyweight exercises into high-intensity interval training (HIIT) or circuit training workouts for added cardiovascular benefits and calorie burn.
-
Combine with other forms of exercise: Bodyweight exercises can be combined with cardiovascular exercises, flexibility training, or other activities of interest. This adds variety to the routine and promotes overall fitness.
-
Track progress: Keep a record of exercises performed, repetitions completed, or workout durations. This helps track progress and provides motivation for continued improvement.
Remember, bodyweight exercises can be adapted to various fitness levels and abilities. It is important to listen to our body and avoid pushing beyond individual capabilities, especially if we have any underlying health conditions or injuries. Seeking guidance from a fitness professional can ensure proper form and technique.
This image is property of www.getbasicidea.com.